You can run both a gateway and portal on the same firewall, or you can have multiple distributed gateways throughout your enterprise.
Portal: Where user can download GlobalProtect client, specify gateway.
An internal gateway is an interface on the internal network that is configured as a GlobalProtect gateway and applies security policies for internal resource access.
Internal gateways are useful in sensitive environments where authenticated access to critical resources is required. The GlobalProtect app connects to the internal gateway after performing internal host detection to determine the location of the endpoint.
External gateway (auto discovery)
An external gateway (auto discovery )resides outside of the corporate network and provides security enforcement and/or virtual private network (VPN) access for your remote users. By default, the GlobalProtect app automatically connects to the best available external gateway, based on the priority you assign to the gateway, source region, and the response time.
External gateway (manual) To configure a manual gateway, you must identify the gateway as Manual when you Define the GlobalProtect Agent Configurations.
License:
secure remote access or VPN solution via single or multiple internal/external gateways, you don't need any GlobalProtect licenses.
However, to use some of the more advanced features (such as HIP checks and associated content updates, support for the GlobalProtect mobile app, or IPv6 support) you must purchase an annual GlobalProtect Gateway license.
About GlobalProtect Licenses (paloaltonetworks.com)
Compatibility Matrix
Where Can I Install the GlobalProtect App?
Configuration
Steps:
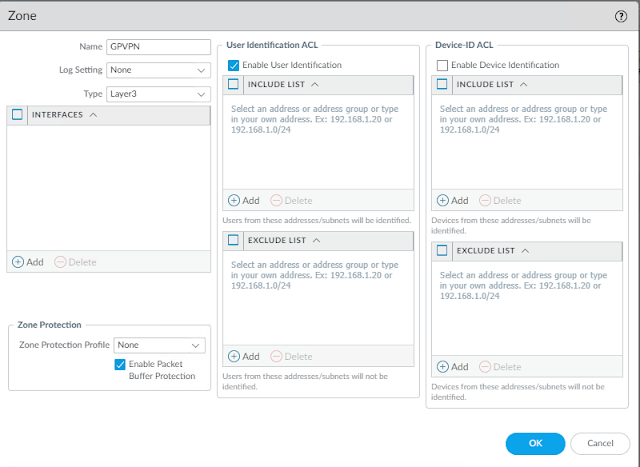
1. Create VPN Security Zone, with User ID enabled
Network>Zones
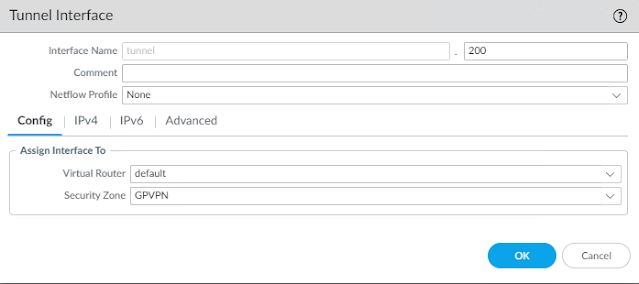
2. Create VPN Tunnel Interface
Network>Interfaces>Tunnel
3.Add Security Policy
3.1 Allow GlobalProtect connects to FW outside interface, this is not required if intrazone-default policy catch the traffic. It is required if a deny access firewall outside IP rule exists.
source zone: untrust
destination zone: untrust destination address: FW outside interface
application: web-browsing (ssl), panos-global-protect
3.2 Allow VPN client to access internal resource souece zone: GPVPN
destination zone: trust
destination address: LAN
application:
Policies>Security
If GPVPN tunnel interface is in Trusted zone, then traffic between LAN and GPVPN will matches Intrazone-default policy.
4. Create an Authentication Profile, attach a server profile.
Device>Authentication Profile
Device>Server Profiles
Bind DN can also use format: ldap@lab.local
5. Create a SSL/TLS Profile, assign a certificate
6. Gateway
Network>GlobalProtect>Gateways
7. Portal
Network>GlobalProtect>Portals
8. Prepare client software, Download and Activate.
Device>GlobalProtect Client
==========================
After connected, on PA routing table, a prefix of VPN pool points to VPN tunnel interface.
Resource List
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClfXCAS
=====Notes===========
1. Enable client disconnect button
portal agent config > App > Connect Method : On-demand (Manual user initialed connection)
=========Troubleshooting==============
1. user is unable to connect to GP portal using browser
fix: added missing security policy to allow connection to FW outside IP with app: web-browsing
2. user is able to connect to GP portal using browser, but can't connect using GP client
fix: added missing security policy to allow connect to FW outside IP with app: panos-global-protect
3. GP gateway configured with AP group, user can't connect with error: "matching client config not found"
fix: authentication profile is missing or has incorrect User Domain
CLI:
> show user group list
cn=contractors,cn=users,dc=sc,dc=local
cn=network admins,cn=users,dc=sc,dc=local
cn=helpdesks,cn=users,dc=sc,dc=local
cn=employees,cn=users,dc=sc,dc=local
Total: 4
* : Custom Group
> show user group name cn=employees,cn=users,dc=sc,dc=local
===============
Internal gateways are not really VPNs. They are used in conjunction with
an "always-on" VPN connection to provide UserID functionality for
PCs/Users connected to your internal networks. Basically, you enable an
always-on VPN configuration and provide an internal gateway with a DNS
record that can only be resolved from your internal network. Then if
your users are in the office, the GlobalProtect client will see that DNS
record, connect to the Internal Gateway, and just report to the
firewall the Username/IP mapping of the host for UserID purposes. If the
user is WFH/on the road, they'll connect to an external gateway and get
the full VPN experience with encryption.
Just used to perform gp agent related functions without
tunneling traffic.
GP related functions: Userid mapping, hip check/reports, scripting (if needed), quarantine identification (if panos 10.x), etc
GlobalProtect supports the following gateway types:
Internal
—An internal gateway is an interface on
the internal network that is configured as a GlobalProtect gateway
and applies security policies for internal resource access. When
used in conjunction with User-ID and/or HIP checks, an internal
gateway can be used to provide a secure, accurate method of identifying
and controlling traffic based on user and/or device state. Internal
gateways are useful in sensitive environments where authenticated
access to critical resources is required. You can configure an internal gateway
in either tunnel mode or non-tunnel mode. The GlobalProtect app connects
to the internal gateway after performing internal host detection
to determine the location of the endpoint. If internal host detection
is not configured, the GlobalProtect app first connects to the internal
gateway followed by external gateway upon connection failure.
External gateway (auto discovery)
—An external gateway
resides outside of the corporate network and provides security enforcement
and/or virtual private network (VPN) access for your remote users. By
default, the GlobalProtect app automatically connects to the
Best Available
external
gateway, based on the priority you assign to the gateway, source
region, and the response time (see
Gateway
Priority in a Multiple Gateway Configuration).
External gateway (manual)
—A manual external gateway
also resides outside of the corporate network and provides security enforcement
and/or VPN access for your remote users. The difference between the
auto-discovery external gateway and the manual external gateway
is that the GlobalProtect app only connects to a manual external
gateway when the user initiates a connection. You can also configure
different authentication requirements for manual external gateways.
To configure a manual gateway, you must identify the gateway as
Manual
when
you
Define
the GlobalProtect Agent Configurations.
The value of adding an internal gateway means that when users are
on the local network, user-to-IP address mappings will be supplied to
the firewall along with device context. This data can then be used as
security policy match conditions, allowing for much more granular,
identity-based visibility and enforcement.
====================
https://live.paloaltonetworks.com/t5/blogs/globalprotect-overview/ba-p/322170
================
PanGPA (PanGP Agent) --- GlobalProtect UI program
C:|Users\username\AppData\Local\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\
PanGPS (PanGP Service) --- GlobalProtect service/daemon program
C:\Program Files\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\
pan_gp_event.log -- high-level log
C:\Program Files\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\
==========Collect GlobalProtect Client Log============
> Settings
> Troubleshooting > Collect Logs, logs will download in a Zip file, extract zip file to see log files
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClaLCAS
In GlobalProtect, debug and dump logs serve different purposes and provide varying levels of detail for troubleshooting. Understanding their differences is crucial for effective diagnostics.
Debug logs are used to capture detailed information about the GlobalProtect application's operations. These logs are typically used for identifying issues during normal operations or when replicating a problem. Debug logs include:
Connection attempts and errors (e.g., PanGPS.log, PanGPA.log).
Interaction between the GlobalProtect filter driver and the system kernel.
General application behavior and events.
Navigate to the GlobalProtect Troubleshooting tab.
Set the logging level to Debug.
Start the logs before replicating the issue and stop them afterward.
Debug logs are less verbose than dump logs and are suitable for most troubleshooting scenarios.
Dump logs provide a more granular and exhaustive level of detail compared to debug logs. They are particularly useful for diagnosing complex issues, such as split-tunneling problems or kernel-level interactions. Dump logs include:
Detailed split-tunnel functionality logs.
Kernel-level interactions captured using tools like DebugView.
Comprehensive packet captures for both physical and tunnel interfaces.
Go to the GlobalProtect Troubleshooting tab.
Set the logging level to Dump.
Reproduce the issue and collect the logs.
Dump logs can generate a large volume of data and may impact system performance. They should only be used when requested by support teams or for in-depth analysis23.
Detail Level: Dump logs are more detailed than debug logs.
Use Case: Debug logs are for general troubleshooting, while dump logs are for advanced diagnostics.
Performance Impact: Dump logs may affect system performance due to their verbosity.
After enabling the desired logging level:
Reproduce the issue.
Use the Collect Logs option in the Troubleshooting tab to bundle logs into a zip file.
Share the logs with support for further analysis13.
By choosing the appropriate logging level, you can efficiently diagnose and resolve issues in GlobalProtect.
=======GP Root Cert==============
This setting is supposed to push CA root cert to Trusted root store on user's PC' . This CA root cert is the GP cert's issuer. However it must be verified by PC's exiting root CA, in this case, lab AD root cert will not be trusted neither installed on user's PC.
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000PN5MCAW
GlobalProtect Stages
- before-login : This is the stage where the Portal pre-login happens during which the client-side reachability (PORT=443, URL=/global-protect/prelogin.esp) and client certificate, etc are checked
- login: This is the stage where the portal authentication happens against the user credentials depending on the authentication profile set
- configuration: This is the stage where the Portal Configuration Digest is pulled from either the cached config or from the actual portal. It also matches the user to any existing cookies if at all present. It then checks for the available gateways.
- before-login: Here it does the Gateway-Prelogin. It checks for the GW connectivity and server certificate verification and then completes the network discovery.
- login: In this stage, it does the Gateway login and checks on the user cookies if at all available. It also gets the IPv4 or IPv6 address for Gateway and user.
- tunnel: This is the stage where the IP-Sec/SSL tunnel is established for the GP traffic. GW configuration is obtained and creates the tunnel accordingly.
- connected: This is the stage where the Gateway is connected.
- host-info: Checks for the Host Information through the HIP checks.
- logout: This is the stage when the user logs out.
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA14u0000001VA3CAM&lang=en_US%E2%80%A9
Loopback interface for GlobalProtect
lookback interface in Untrust zone
GP connection will go through full threat prevention before hit lo interface.
Manually Sync LDAP Group Mapping
You can refresh the user-group-mapping on the PAN by issuing the following the command:
> debug user-id refresh group-mapping all ..... This command will fetch the only delta values or the difference.
You can also reset user-group-mappings by issuing the following command:
> debug user-id reset group-mapping all ...... This command will fetch the entire group mappings once again.
Pre-logon is a connect method that establishes a VPN tunnel before a user logs in. The purpose of pre-logon is to authenticate the endpoint (not the user) and enable domain scripts or other tasks to run as soon as the endpoint powers on. Machine certificates enable the endpoint to establish a VPN tunnel to the GlobalProtect gateway.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k2Y2L8wiMdI
Portal configuration:
Policy:
Troubleshooting GlobalProtect
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClkBCAS
======Log===============
1. When a new user accesses GUI portal to download client.
2. when you input vpn URL from GP client then logged in.
Auth Cookie
Cookies are stored locally on the user's machine:
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\
The filename usually starts with PanPUAC_ followed by a unique identifier
Automatic Restoration of VPN Connection Timeout
Network > GlobalProtect > Portals > "PortalName" > Agent > "AgentConfig" > App > App Configurations > "Automatic Restoration of VPN Connection Timeout"
controls how long the GlobalProtect app will attempt to automatically reestablish a VPN tunnel after it has been disconnected due to network instability or endpoint state changes. Default: 30 minutes
Example: If set to 30 minutes and the tunnel is down for 15 minutes, GlobalProtect will attempt to reconnect. If it's down for 45 minutes, it won't.
GPA:
URL=/global-protect/prelogin.esp
GPS:
----Portal Pre-login starts----
...
prelogin to portal result is
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<prelogin-response>
<status>Success</status>
<ccusername></ccusername>
<autosubmit>false</autosubmit>
<msg></msg>
<newmsg></newmsg>
<authentication-message>Enter login credentials</authentication-message>
<username-label>Username</username-label>
<password-label>Password</password-label>
<panos-version>1</panos-version>
<saml-default-browser>yes</saml-default-browser>
<server-ip>204.x.x.x</server-ip><cas-auth></cas-auth>
<saml-auth-status>0</saml-auth-status>
<saml-auth-method>REDIRECT</saml-auth-method>
<saml-request-timeout>600</saml-request-timeout>
<saml-request-id>0</saml-request-id>
<saml-request>aHR0cHM6Ly9sb2dpbi5taWNyb3NvZnRvbmxpbmUuY29tL2Y5MWE4YTRhLWMyMDQtNDA1Zi05ZGQ2LWYzNWEzODA0YzU5My9zYW1sMj9TQU1MUmVxdWVzdD1uVkpCYnNJd0VQeEs1SHRpeDBtQVdJQkU0VkFrcWtZazdhR1h5amdic0pUWTFPdFU3ZTlMb0ZYcGhVT1BxeDNOek03c0ZHWFhIc1dpOXdlemhiY2UwQWNmWFd0UW5CY3owanNqckVTTndzZ09VSGdseXNYRFJ2Q0lpYU96M2lyYmttQ0JDTTVyYTViV1lOJTJCQks4Rzlhd1ZQMjgyTUhMdyUyRm9xQVVRZlVPT28wWVFRdktPNjFraTdJQiUyRnhsWkV5a3AwalNoQXp0bnRDem9ZbG1TWUhWeXBJMGN1SCUyQlpXcnZYSnVxMGNoWnQ0NjFwdFlGSTJZNDJlU3duTXBXaDRpd05VNVkxWVY3WG83QkpNcGxNV0txeVBLSERhWndFNjlXTXZJNG5QR3NTdVpNcTVydFJNNnByRGpGd25tZFFRODdxRXd5eGg3VkJMNDJmRWM1NEZzWXNaSk1xSG9zc0Z6eDVJVUh4bmNTZE5yVTIlMkI5dXg3UzRnRlBkVlZZVEZZMW1SNEJrY25rODhBY2g4T2pnVVoyRjNWY2R0V3ZuVEFabiUyRk0lMkZFcHZkS2RYNmElMkZ2ekglMkZBZyUzRCUzRCZSZWxheVN0YXRlPVZSZ0FBTEROM1dnelpEZGxPVFExTmkxak1tVmhMVFEwTmprdE9USXdZUzAwTm1GaU5ETmtNVFZtTVRNdw==</saml-request>
<auth-api>no</auth-api><default-browser>no</default-browser><region>CA</region><cas-embedded-browser>no</cas-embedded-browser></prelogin-response>
show system software status
debug software restart process xxx
tail follow yes mp-log logfile
Gateway detail configuration from CLI:
show global-protect-gateway gateway xxx
debug software logging-level show level service ikemgr
debug software logging-level set level debug service ikemgr
Upload GlobalProtect image from CLI:
admin@PA440-1> scp import global-protect-client from admin@192.168.2.167:/PanGP-6.2.8-c263
admin@192.168.2.167's password:
PanGP-6.2.8-c263 100% 247MB 60.8MB/s 00:04
PanGP-6.2.8-c263 saved
admin@PA440-1> request global-protect-client software activate file PanGP-6.2.8-c263
Executing this command will activate a new version of GlobalProtect client software that will be downloaded on GlobalProtect users' computers when they connect next time. Do you want to continue? (y or n)
client package activate job enqueued with job id 10. Run 'show jobs id 10' to monitor its status.
10
admin@PA440-1>
or Activate from file in GUI.






























Comments
Post a Comment